Keyword cannibalization is a common phenomenon in SEO that affects a surprisingly large number of website owners – whether they know it or not. If you carry out a basic SEO competitor analysis for specific keywords within your industry, you’re bound to come across websites affected by keyword cannibalization. And although keyword cannibalization isn’t the end of the world, it’ll certainly have an impact on your site’s SEO performance.
So, whether you’re currently trying to fix keyword cannibalization on your own website or want to learn how to deal with it just in case it happens to you – you’re in the right place. In this article, we’re going to take a closer look at:
- The impact of keyword cannibalization on SEO performance
- How to fix cannibalised keywords
- How to prevent keyword cannibalization in the future
And in the end, we’ll answer some of the most common questions around keyword cannibalization. But before we do that, let’s first take a look at what keyword cannibalization is and when it happens.
What Is Keyword Cannibalization and When Does it Happen?
Keyword cannibalization refers to a situation where two or more pages on the same domain target the same or similar keyword(s) or phrase(s). This can confuse the search engines and cause two (or more pages) that target the same keyword or phrase to compete against each other.
Over time, instead of climbing up the SERP, the pages will eat away at each other, causing each other’s rankings to drop, ultimately affecting your site’s SEO performance. Keyword cannibalization often isn’t intentional. It typically happens when you:
- Create a new page to replace an old one, without setting up any redirects
- Have been publishing content on similar topics for a long time
- Optimise similar pages for the same or similar keywords
- Don’t optimise your subcategory pages
- Faceted navigation is not correctly managed and opens several variations of pages to indexing, which could risk being positioned on the same query
- The tree structure of your site is not clearly defined
Fortunately, keyword cannibalization isn’t the end of the world for your website. However, if it goes unnoticed, it can take a toll on your site’s SEO performance. In the section below, we’re going to take a closer look at what you can expect if your site is affected by keyword cannibalization.
The Impact of Keyword Cannibalization on SEO Performance
Having worked on countless SEO campaigns at our SEO agency, we’ve found that although keyword cannibalization doesn’t typically affect the entire site, it can massively impact the performance of individual pages. And if those pages are significant enough for the traffic or revenue your website is generating, it can be a problem.
There are many different ways keyword cannibalization can affect your SEO performance, including:
- Confuse Google which of the duplicate or near-duplicate pages it should rank the highest
- Make your pages compete against themselves until they no longer rank
- Reduce click-through rate (due to not ranking the most relevant page)
- Decrease conversion rates (this usually happens when users land on a page that doesn’t fully satisfy intent)
- Dilute keyword ranking power and open the door for the competition to rank higher than you
- Reduce the effectiveness of internal linking and make it more challenging
How to Fix Cannibalised Keywords
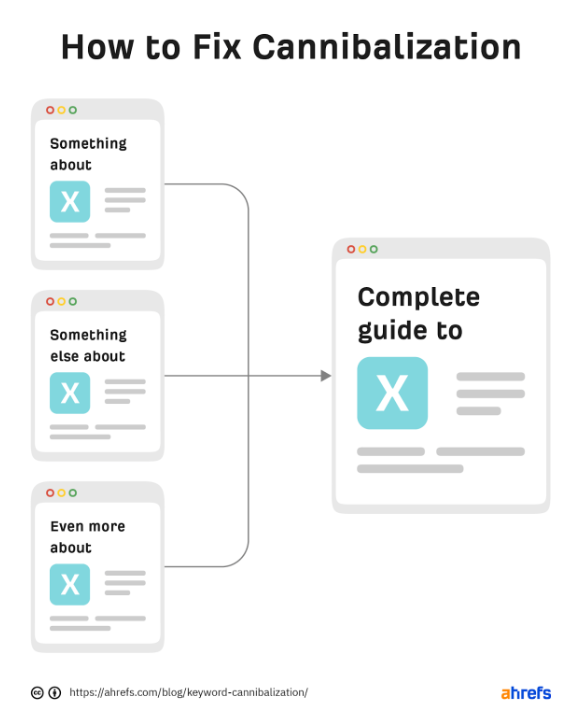
If you have a case where two pages are competing against each other for the same or a similar keyword or phrase, the first thing you need to do is pick the page that you want to keep. Once you’ve made a decision, you need to make it abundantly clear to Google so that it knows which of the two (or more pages) to rank the highest in the SERP.
There are a handful of ways you can go about doing that, and it’ll all depend on your situation. Here are a few common solutions:
- Redirects: This strategy is best when you have similar or duplicate pages on the same topic that you don’t need to keep
- Optimise Links & Existing Content: This approach is best when you’d like to keep all the affected pages
- Canonical Tags: A possible solution if you have duplicate pages that you want to keep
- Noindex Tags: This is a last-resort keyword cannibalization fix in case you have similar pages that you want to keep, but none of the solutions above work
To give you a better idea of the ins and outs of each of the above solutions, let’s take a look at each one in more detail:
Redirects
If you have multiple pages that target the same or a similar keyword, you can choose to only keep one of them. In such a case, redirecting all of the other pages to the one you decide to keep will resolve your keyword cannibalization problem.
To begin this process, you first need to decide which page you want to keep. It’s worth noting that you shouldn’t make this decision blindly. Pick the page that has the biggest potential to perform. Some things to look at when deciding which page to keep include:
- The number of backlinks
- Current ranking in the SERP
- The traffic that the page is currently getting
- The quality and depth of the content
Side note: Although you can simply redirect all the pages to your preferred page, there is one optional step that we recommend taking. Before doing the redirects, you should take a look at the content on the cannibal pages and see if any of it is worth adding to your preferred page. That way, your existing content won’t go to waste and will only make your preferred page stronger.
Once you’ve made the decision on which page to keep, here is what you need to do next:
- Publish the new version of your preferred page on your preferred URL
- 301-redirect all of the cannibal pages to the page you want to keep
- Check if there are internal links to redirected pages and update them
- Remove the URLs of the redirected pages from your sitemap
Optimise Links & Existing Content
One unique and quite confusing scenario of keyword cannibalization is when a more authoritative page ranks higher than a dedicated page for a specific keyword. For instance, if you have a “/shoes/” page with stronger SEO signals that touches upon running shoes, it may outrank your “/shoes/running/” subcategory page for the “running shoes” keyword.
This tends to happen when Google fails to recognise the more relevant result in the SERP. To fix such a case of keyword cannibalization, you should tell Google which page to rank for that keyword. You can do this by building out a link from the cannibal page – in this case “/shoes/” to the target page ‘/shoes/running/” using “running shoes” as anchor text.
Canonical Tags
If you have duplicate or near-duplicate pages that you want to keep live on your website but you don’t necessarily want them to add any SEO value, you can use canonical tags. What canonical tags do is point Google to the main version of the pages that are causing the cannibalization issue.
They also let Google know which page should receive all the ranking power, rather than diluting it across numerous URLs. Some examples when using canonical tags to resolve keyword cannibalization makes the most sense include:
- For landing pages designed to convert paid traffic
- For alternative pathways to the exact same product page or category
- For pages that have complex URLs (for instance – “/laptops/gaming/screensize=17&color=black)”
Noindex Tags
If none of the above recommendations work for you, your best bet is to instruct the search engines not to index any of the similar or duplicate pages. To do that, you’ll use the noindex tag, which is a piece of HTML code.
Although telling Google not to index your duplicate or similar pages will resolve the cannibalization issue, it should only be used as a last resort. The reason for this is because when you hide a page from Google using the noindex tags, it won’t forward any of its ranking signals to the main page.
That’s why if you plan on implementing noindex tags, they should only be used on pages that either have very thin content, don’t drive any traffic, and have no backlinks.
How to Prevent Keyword Cannibalization
To avoid keyword cannibalization, it’s a good idea to keep track of the content that is being published on your website. That way, you can always refer to all of the pages that have been published before you create new or optimise existing content.
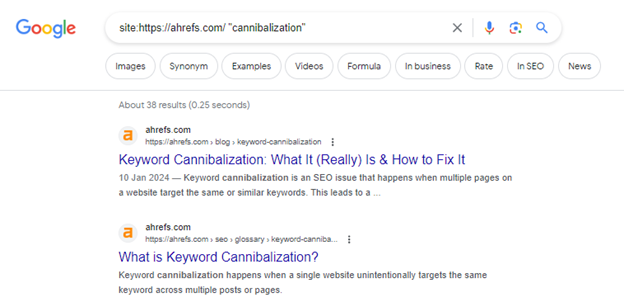
We’d also suggest that you check the SERP and see if you already have pages ranking for the keyword that you want to target. To do that, head over to Google, and write “site:[your domain] [target keyword].”
And if you come across a page that is already ranking for that keyword, you should optimise it rather than creating a new one. Or if you want to create a new page anyway, you should take care of the necessary redirects and tags so you can launch the new page without confusing Google and potentially harming the SEO performance of your existing page. We also recommend you refer to a semantic audit in order to put in place a content hub: this strategy will aim to target the maximum number of keywords related to a common topic while avoiding keyword cannibalization thanks to careful planning of content creation and optimisation.
FAQs About Keyword Cannibalization
Is Keyword Cannibalization Good Or Bad?
If you’re trying to rank high on Google (or any other search engine, for that matter), keyword cannibalization is considered bad and should be avoided at all costs. The reason for that is that it creates competition between two (or more) pages which target the same or a similar keyword or phrase.
As a result of that, search engines will have a hard time figuring out which of the two (or more) pages to rank, effectively triggering the process known as keyword cannibalization. Once the process of keyword cannibalization begins, the pages going after the same or similar terms will start to eat at each other. Over time, instead of going up in the SERP, they will drop and won’t recover until the issue is resolved.
How Do You Identify Keyword Cannibalization?
There are a handful of different ways to identify keyword cannibalization. If you’re well versed in SEO, you can review the content on your website manually. This includes everything from the actual on-page content to the titles and meta descriptions.
You can also carry out your own SERP analysis, where you can Google specific short or long-tail keywords and see if Google ranks two or more of your pages for those specific keywords. If the answer is yes, you may have an issue.
If you don’t have the time or don’t want to take your chances, the second best way to identify keyword cannibalization is to carry out an SEO audit using SEO tools. You can either use free SEO tools in the likes of the Google Search Console and Google Analytics or use third-party paid tools like SEMRush.
These tools can help you analyse the keywords that each page is ranking for and identify any instances where several different pages are going after the same or similar search query.
What Is An Example Of Keyword Cannibalization?
A very basic example of keyword cannibalization is having two different pages on the same domain – one focused on “best tennis shoes for beginners” while the other one is focused on “top running shoes for new tennis players.”
Although the keyphrases are different, they are very similar since they target practically the same audience. This can lead to competition between the two pages. As a result, over time, their rankings will drop, and their visibility will decrease, ultimately affecting the overall effectiveness of the content.
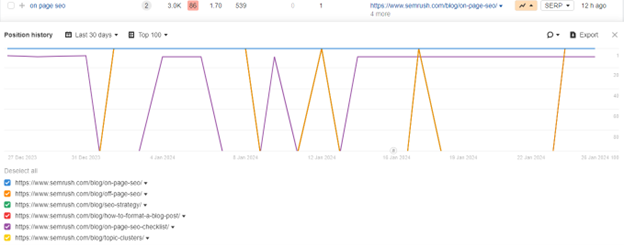
What Is Keyword Cannibalization In Semrush?
SEMRush, like most SEO tools, has a feature that can help users identify keyword cannibalization on their websites. In SEMRush specifically, keyword cannibalization can be identified by analysing the positions of the different pages on your site for specific keywords.
This can be done using the Position Tracking tool. It’s designed to keep track of your site’s content and flag potential keyword cannibalization issues, which you can find in the Cannibalization Report inside SEMRush.
Having this type of insight into your keyword rankings will allow you to assess and address any potential cases of keyword cannibalization. This will prevent pages that could be ranking high on Google from competing against each other, resulting in better overall SEO performance.











